Steps towards gene therapy for diabetic retinopathy
Dr Guei-Sheung Liu, Menzies Institute for Medical Research, University of Tasmania, Tasmania
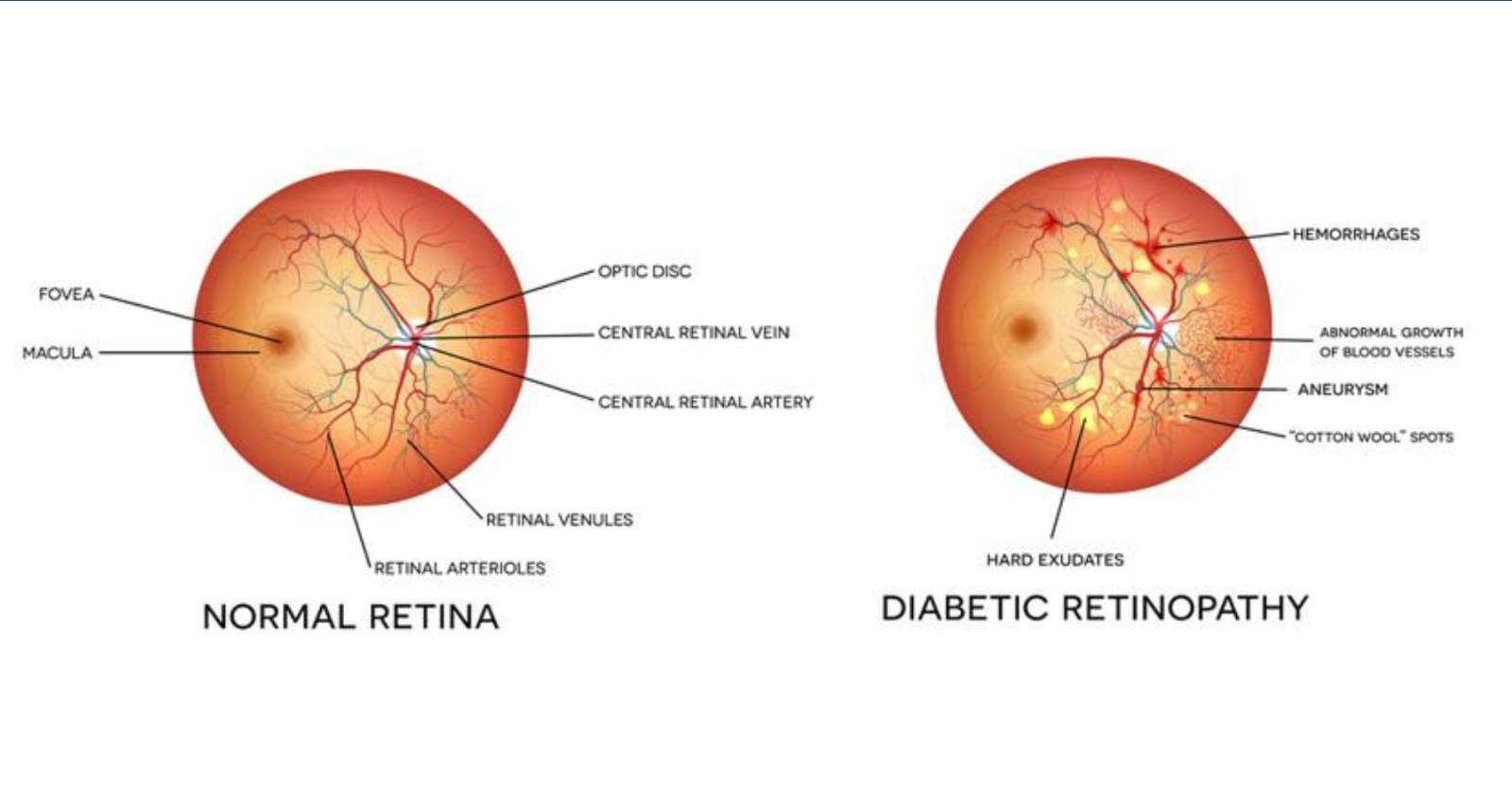
Diabetic retinopathy is a frequent complication of diabetes and is a leading cause of vision loss worldwide. Treatments for diabetic retinopathy include anti-VEGF treatments (such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) neutralising proteins) however these require ongoing eye injections and carry risks and are expensive.
In this research project a novel approach for delivery of VEGF inhibition into the cells will be investigated.
“We will use an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector to deliver an intracellular VEGF decoy receptor (Flt23k) that neutralises intracellular VEGF and prevents its secretion,” said Dr Liu.
The therapeutic efficacy and effect of retinal vascular hyper-permeability will be evaluated in a diabetic animal model.
“Vision loss from diabetic retinopathy is a global health concern, significantly impacting the quality of life of patients. Our project will validate a new strategy for blocking VEGF in the eye, with the advantage that it is longer lasting and can be switched on only when needed,” said Dr Liu.